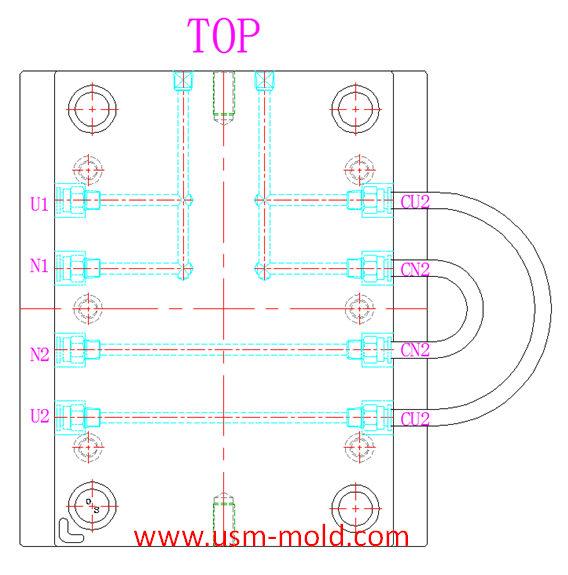
Different treatment of plastic injection mold cooling system principles
Different treatment principle:
1. The mold temperature is different according to the different plastics, when the plastic requires the molding temperature of the mold to be ≥80°C, the mold must be heated.
2. The temperature of the cavity should be higher than the temperature of the core, and the temperature difference is generally 20~30℃.
3. For texture cavity with EDM markson the surface, the cavity temperature should be higher than the general polishing surface, when the cavity must be filled with hot water or hot oil, the general temperature difference is about 40 ℃.
4. For plastic parts with dense meshes, such as speaker shell, the material flow resistance in the mesh area is relatively big and it is difficult to fill. Increasing the mold temperature in this area can improve the filling conditions, the cooling channel in the mesh area is required to be separated from the cooling channel in other areas to flexibly adjust the mold temperature.
5. The mold temperature also depends on the surface quality of the plastic part and the structure of the mold, when designing the temperature control system, it should be targeted from the perspective of the wall thickness of the plastic part, the thick wall should be cooled to prevent shrinkage and deformation; Considering the complexity, cooling should be strengthened at the place where the cavity height fluctuates greatly; the heat of the gate inserts should be strengthened; the cooling channel should be avoided as far as possible through the location of the weld line and the location of the thin wall to prevent the defect more obvious.
6. When the mold temperature is required to be high, such as 70°C or higher, the temperature control of the mold should pay attention to the following:
a. The choice of mold material requires high wear resistance and hardness, heat treatment must be carried out, and the machinability before heat treatment is good.
b. The sealing ring in the mold cooling system should be made of heat-resistant material which is to add the lead.
c. It needs to be a cooling channel between the sliding parts of the mold (such as guide pillar, guide sleeves, etc.) to prevent thermal expansion and contraction from causing movement of moving parts to lock.
d. The shutting-off part of the mold will also strain the shutting-off surface due to thermal expansion and contraction, the shutting-off angle can be appropriately increased to reduce the shutting area, the peripheral interface is formed by inserting.

Limitations of gas-assisted injection molding technology
Apr 25, 2022Gas-assisted injection molding technology has obvious advantages in thick wall thickness and pipe parts, but this technology still has many limitations, which are mainly reflected in the following...view
Unique Solutions Mold Profile
Dec 27, 2021USM (UNIQUE SOLUTIONS MOLD LIMITED) was founded in 2012 and is located in Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, a famous mold manufacturing province in China, the plant covers an area of 3500 square...view
Vacuum venting mold design for plastic molded parts
Mar 23, 2022There are some regular venting way which are parting surface venting, insert venting, insert pin venting and well-ventilated steel, but there is a special way is vacumm venting, it will need vacumm...view
The design principle of the exhaust slot
Mar 6, 2022The exhaust system of plastic molds is also very important, if the product has air trapping or exhaust system is not suitable will have a big impact on injection molding production and product...view_20250317091228A019.jpg)
Main application of gas-assisted molding technology
Apr 7, 2022Gas-assisted molding has a particularly obvious effect on the material saving of tubular and rod-shaped plastic parts, such as car handles, seat armrests, window frames, and wood-like furniture, the...view
Conformal cooing channel of plastic injection mold
Feb 23, 2022The conformal cooling gate is a new type of mold cooling gate based on 3D printing technolog, because of its processing characteristics, the conformal cooling gate can fit the shape of the product...view
 English
English русский
русский
_20250310164515A048.webp)
