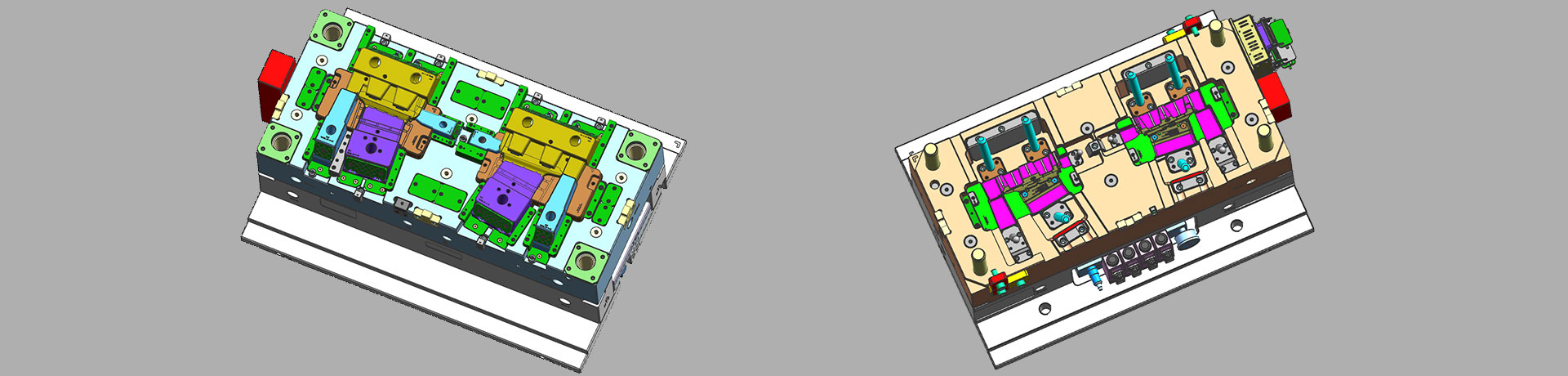
Key points of plastic injection mold runner system
The sub-runner is a transitional channel between the main runner and the gate, as the sub-runner is the longgest part of gating system, so it is very important to enhance the parts quality and improve the productivity by reducing sub-runner process and flow resistance.
Sub-runner requirements:
① Bring the air in the gating system and the cold material at the front side of the melt into the cavity as less as possible to improve the molding quality.
②The runner resistance to the melt should be small, and the volume flow rate should be large to reduce the pressure and temperature loss when the melt flows through the runner.
③The solidification time of the runner should be later than the solidification time of the melt in the cavity to facilitate feeding.
④Ensure that the melt enters each cavity or every corner of the same cavity quickly and evenly.
⑤ The length of the runner should be as short as possible, and its volume should be as small as possible.
⑥The shape and size should be convenient for processing and tool selection.
⑦The upper-level runner is 10%~20% larger than the next-level runner.
Factors affecting the sub-runner design:
①The geometric shape, wall thickness, size, stability, internal quality and appearance quality requirements of plastic parts.
②The variety of plastics, that is the fluidity, melting temperature and melting temperature range, solidification temperature and shrinkage rate of the plastic.
③The pressure, heating temperature and injection speed of the injection molding machine.
④ Falling off method of main runner sub runner.
⑤The cavity layout, the gate location and type.
Key points of sub-runner design:
Cross-sectional area: as small as possible under the conditions of the injection process.
Distribution: compact and symmetrical, minimize the total area of the forming area.
Shape: The ratio of cross-sectional area to perimeter is as big as possible.
Length: as short as possible; the length of the runners of each cavity should be as equal as possible.
Steering: as few times as possible and rounded transitions.
Roughness of the inner surface: It is not necessary to be very light, so that the outer layer of the material flow forms a cooling layer for heat preservation, Ra=0.8~1.6μm.
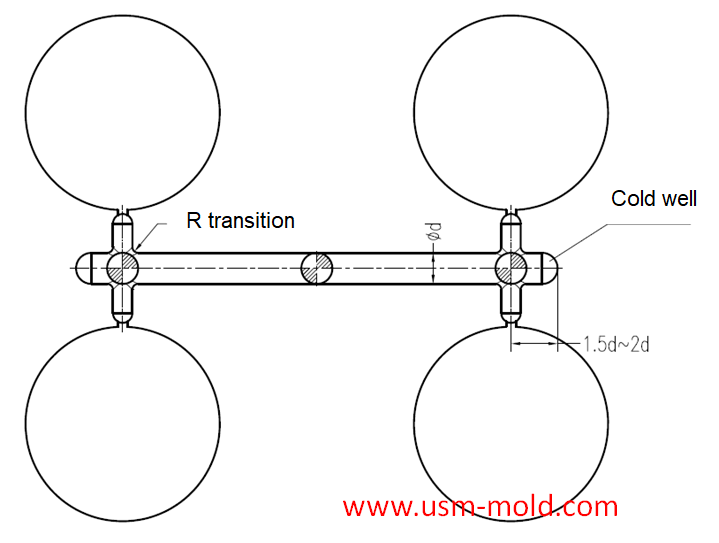
Condensate ejection: This is particularly desirable when a sprue puffier is used when sub-runner is in cavity side or it is long.
The end of the sub-runner should be provided with a cold well and exhausting-slot .
Design principle of plastic injection mold cooling system
Feb 13, 2022Design principle of cooling system In order to improve the efficiency of the cooling system and make the cavity surface temperature distribution even, the following principles should be followed in...view
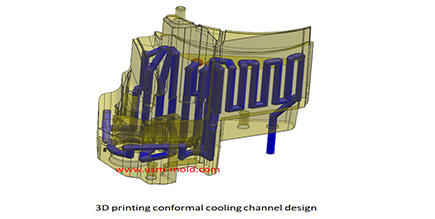
Conformal cooing channel of plastic injection mold
Feb 23, 2022The conformal cooling gate is a new type of mold cooling gate based on 3D printing technolog, because of its processing characteristics, the conformal cooling gate can fit the shape of the product...view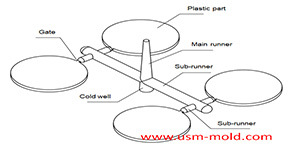
Design principles of plastic injection mold runner system
Jan 6, 20221. Quality first The design of the gating system has a big influence on part quality, firstly the gate should be set at the easiest part of the plastic part to be removed, and at the same time, the...view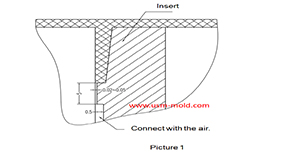
Venting insert design of molded parts
Mar 13, 2022In the thin-walled cavity, the end of the melt flow, the bottom of the blind hole of the mold cavity, the end of the solid column of the plastic part, the bottom of the plastic part rib and screw...view
Venting of parting surface
Mar 7, 2022The exhaust slot on the parting surface is easy to clean and processing, also not easy to be blocked, and has a good exhaust effect, it is the main area where the gas is exhausted, so the exhaust from...view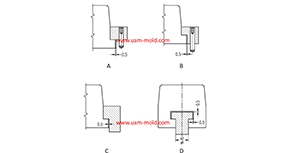
The T slot of slider and guider designing tips
Dec 18, 20231. The T slot of slot should be designed according to the picture 1, If there is a relatively high slider, the slider T slot is not high enough which will cause the center of gravity to be unstable,...view
 English
English русский
русский